Aliada is advancing therapeutic candidates using the Modular Delivery (MODEL) platform, a differentiated and novel blood-brain barrier (BBB) crossing technology. Originally developed by Janssen, the platform can carry a wide range of cargoes into the brain. MODEL addresses the critical need for efficient and versatile delivery technologies for large molecules, which are currently limited in their effectiveness for CNS indications by factors such as extremely low trafficking across the BBB with antibodies, and the need for intrathecal delivery of oligonucleotides.
our platform
The MODEL platform
The MODEL platform:
Engineered for high-precision CNS delivery
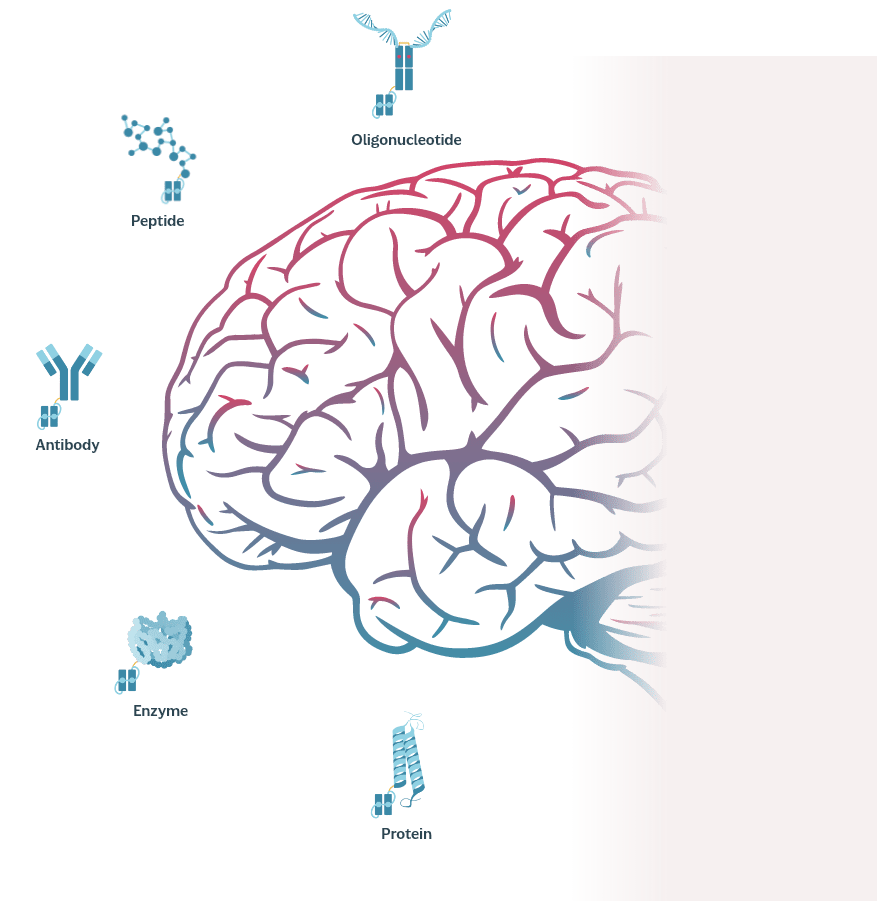
The MODEL platform is designed to have unparalleled utility inside the brain, where it can direct cellular uptake of cargoes. The platform’s modular design gives it greater functionality, versatility and performance compared with other BBB-crossing technologies. We currently have active preclinical programs across multiple cargo types and neuroscience disease areas.
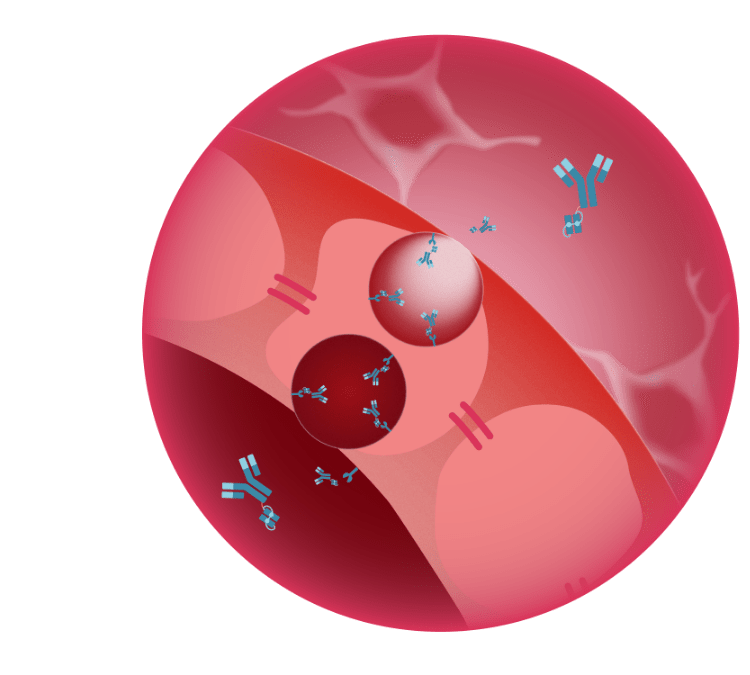
Crossing into the brain:
Receptor-mediated transcytosis
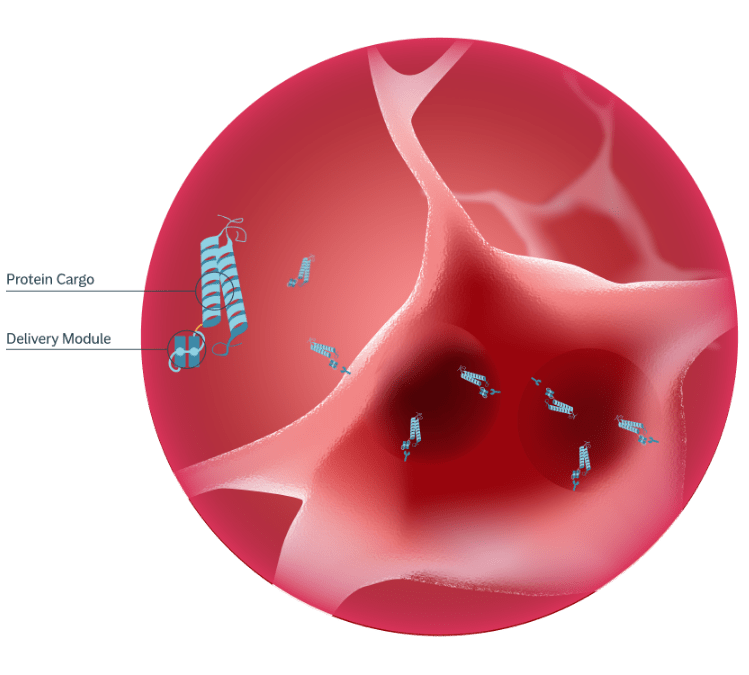
MODEL leverages the transferrin and CD98 receptors (TfR and CD98), which ferry iron and selected amino acids from the peripheral bloodstream into the brain. To cross the BBB, engineered protein domains with cargoes attached first bind to these receptors on the epithelial cells that make up the BBB. This binding initiates the formation of endosomal compartments that migrate through the cytoplasm and cross into the brain via transcytosis.
-
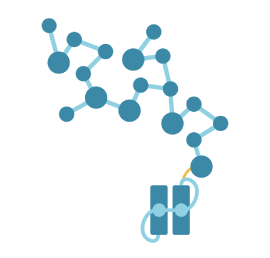
Oligonucleotide
-
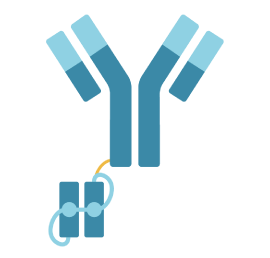
Peptide
-
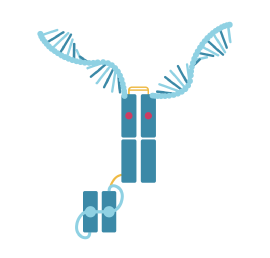
Antibody
-

Enzyme
-
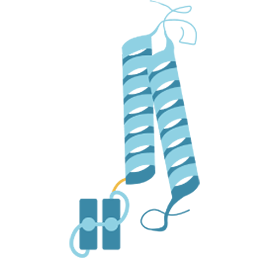
Protein
Delivery within the brain:
Uptake by CNS cells
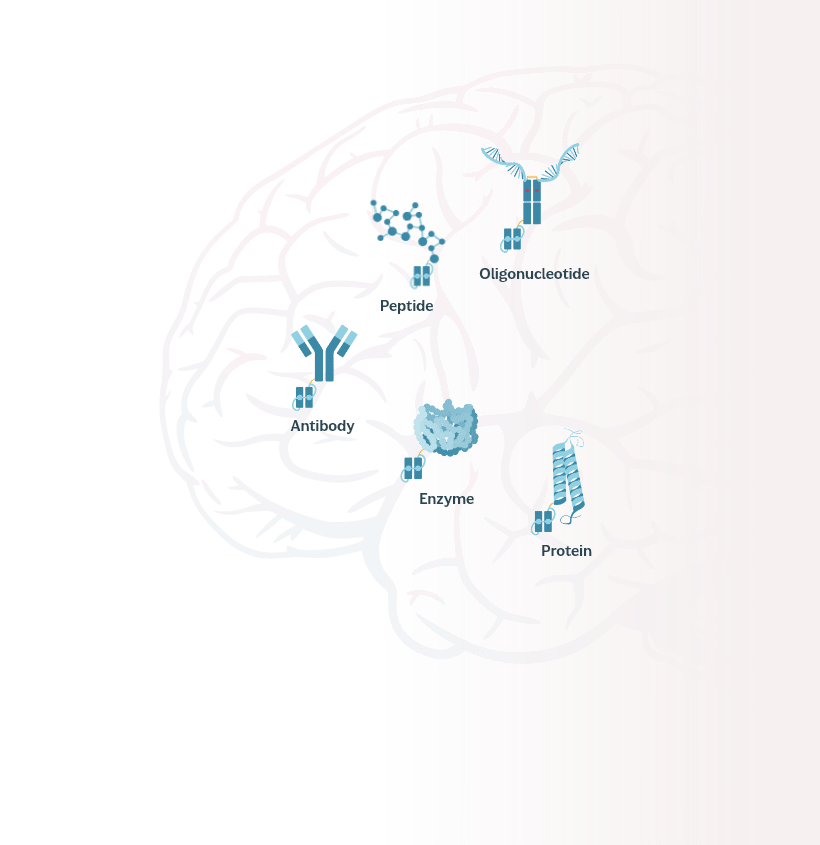
Because TfR and CD98 are expressed on resident cells inside the brain as well as the epithelial cells of the BBB, MODEL can also mediate cargo uptake by neurons, microglia and macrophages through a process known as receptor-mediated endocytosis.
-

Oligonucleotide
-

Peptide
-

Antibody
-

Enzyme
-

Protein
Design Features:
Benefits of Modularity
The modular structure and stable design of the MODEL platform together create a powerfully versatile system for CNS drug delivery, designed with the ability to take a modality-agnostic approach to a given disease target or area of therapeutic interest.
For example, the platform enables optimization for exposure needs and therapeutic functionality, through its ability to interact with either of two distinct receptors (TfR and CD98) and bind a variety of therapeutic cargoes. Aliada is leveraging specific insights on each receptor target to develop differentiated therapeutics, such as TfR affinity and kinetics and an improved CD98 pharmacokinetic profile for greater brain exposure.
The receptor-binding elements of the MODEL platform, known as Delivery Modules, enable novel engineering features for better stability, manufacturing and therapeutic profiles.
The flexibility of this system, as summarized below, enables optimization of modality, Delivery Module design, transport receptor and other parameters for a given CNS target.
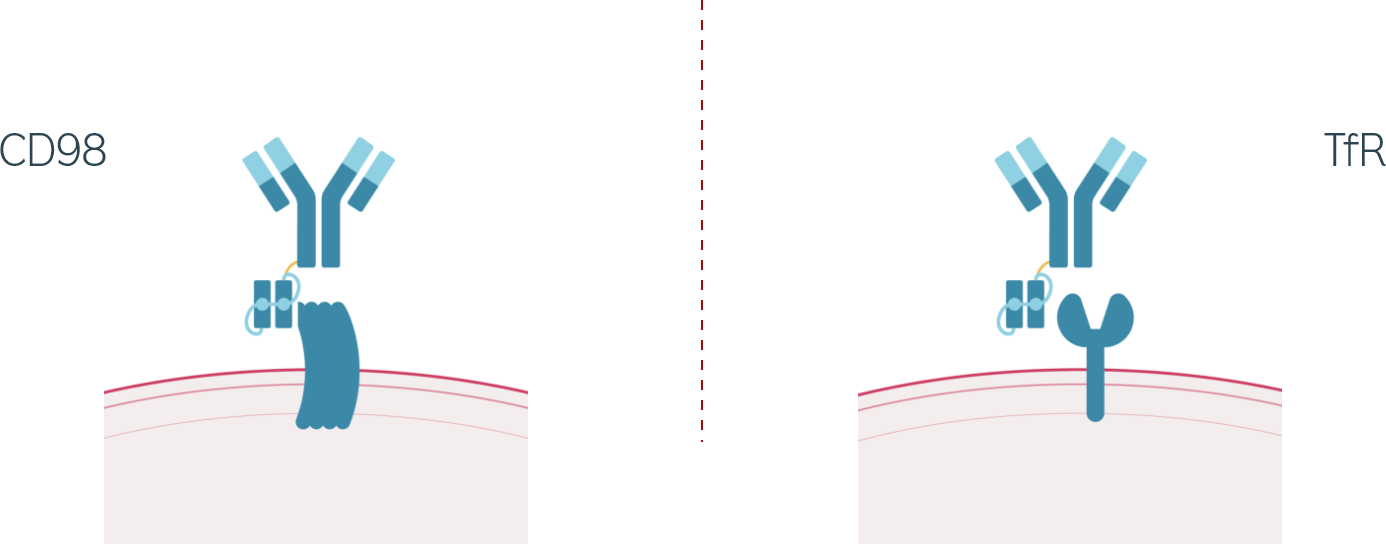
SPECIFIC AND CUSTOMIZABLE TARGETING
to endogenous receptor sites via two distinct receptors

VERSATILITY IN DELIVERY
of multiple cargo types
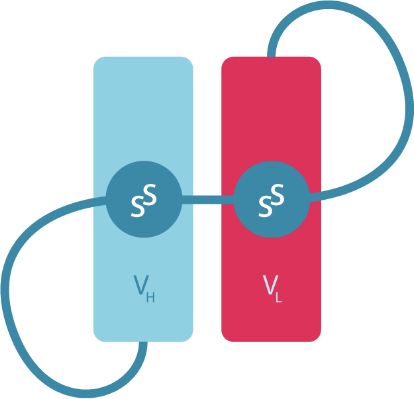
STABILITY OF STRUCTURE
when using scFv delivery modules via disulfide stapling
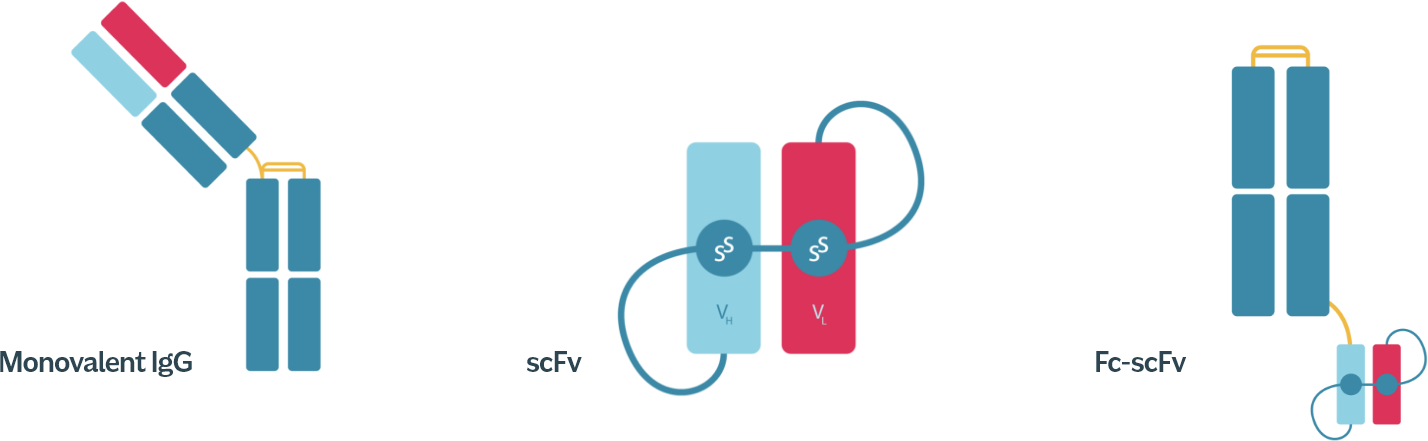
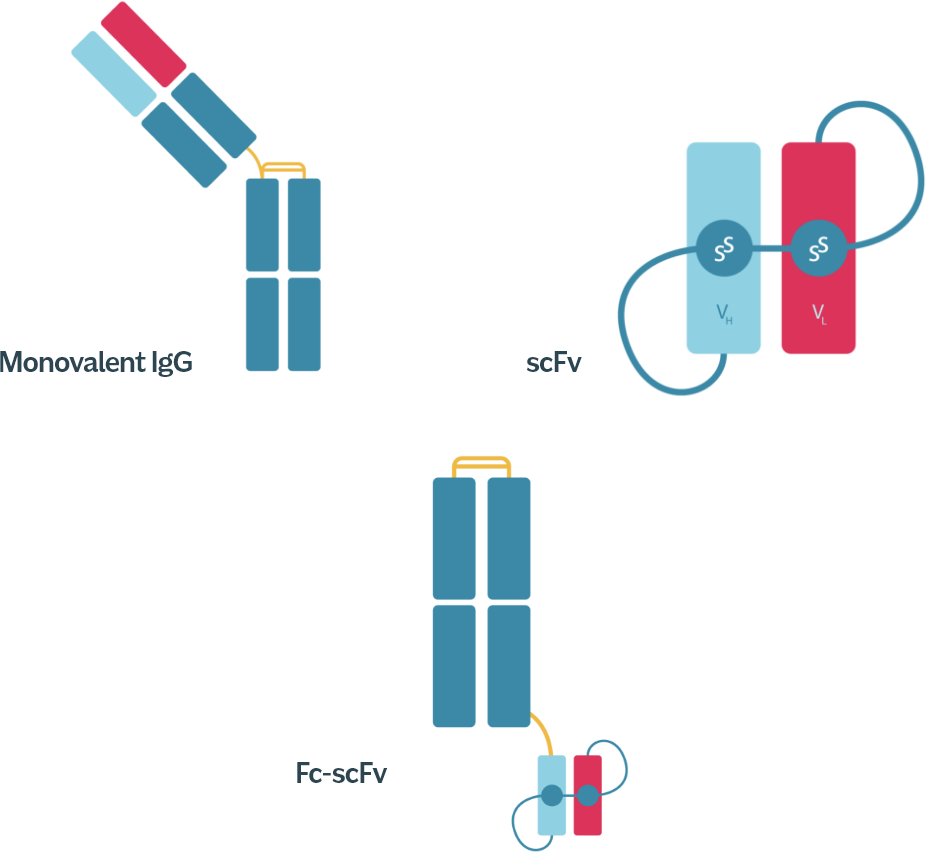
ADAPTABLE DESIGN LANDSCAPE
enabling expression of delivery modules in multiple formats
OPTIMIZED ENGINEERING OF Fc DOMAIN
for preferred target clearance, extended half-life and dosing efficiency